Roman Britain (43 AD - 410 AD)
|
Key Questions: 1. The Roman invasion of Britain
|
How did the Romans build such a big empire?
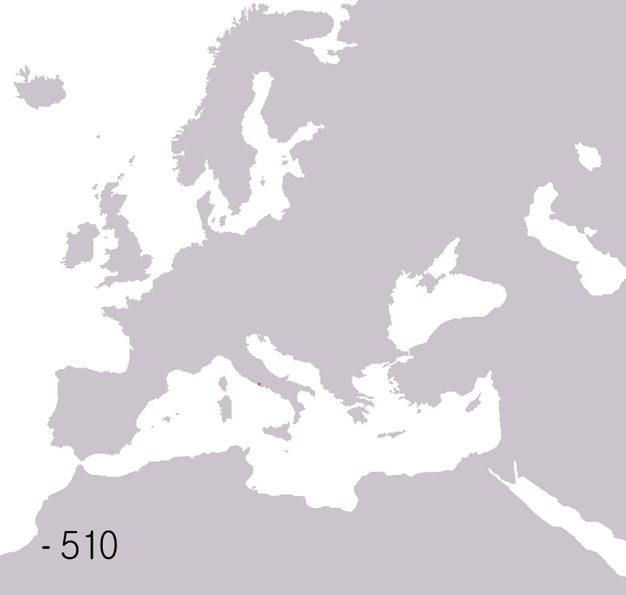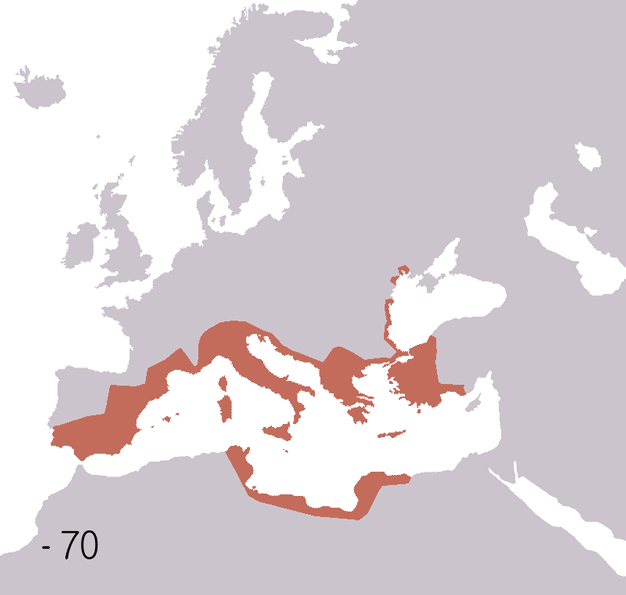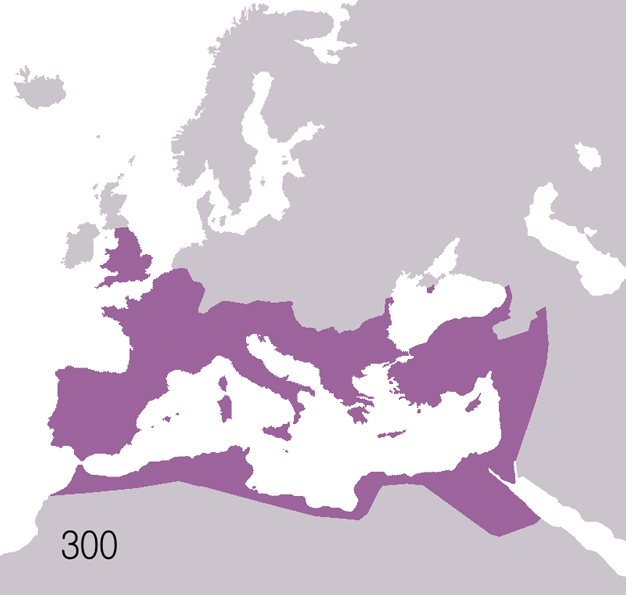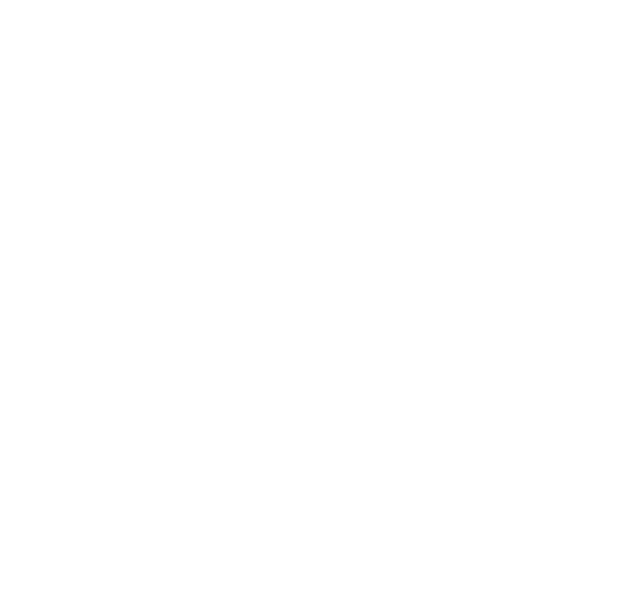
The Romans built up their empire through conquest or annexation between the 3rd century BC and the 3rd century AD. At its height, the Roman Empire stretched from north-western Europe to the Near East and encompassed all the lands of the Mediterranean. The control of the empire depended on a tightly controlled system of administration, a strong and disciplined army, and excellent communications. Provinces of the empire were controlled by Roman governors appointed by the emperor. The Roman army built a number of strategically placed forts to ensure that the empire was defended against hostile local peoples, and an efficient network of roads was built both to allow troops to move swiftly within the empire and to facilitate trade. Taxes levied and valuable commodities such as grain, minerals, and slaves enriched Rome and financed its army. The many diverse peoples and cultures whose countries became part of the Roman Empire were united by Roman culture and Roman ideals of government and citizenship.
When and how did the Romans invade Britain?
 |
 |
In 54 BC, Julius Caesar failed in attempt to invade Britain. In 43 AD, Emperor Claudius organised the final and successful Roman invasion of Britain. General Aulus Plautius led four legions with 25,000 men, plus an equal number of auxiliary soldiers. They crossed the Channel in three divisions, landing at Richborough, Dover, and Lympne. It took about four years for the invaders to finally gain control over southern England, and another 30 years to conquer all of the West Country and the mountains and valleys of Wales.
Why did the Romans invade Britain?
Study the following presentation, then click "Continue" button in the instruction pop up window to complete the interactive diagram below.
Were the Romans civilised?
There is much to prove that the Romans were civilised, for example, their technology, architecture, philosophy, military, economics, law making and government were quite advanced for the day. They introduced the calendar that we still use and the way of their government was used as a bench mark by modern civilisation. However, there are aspects of their life that would consider very uncivilised, such as gladiators, slavery, treated women as little more than property and routinely practiced genocide.
The following presentation provides useful sources for your essay about Roman civilisation.
Roman Invasion of Britain
How did the Romans control Britain/respond to rebellion?
The Romans had a large, well equipped, well trained and disciplined army that was used to control Britain. The Roman Army built a number of strategically placed forts to defend themselves against hostile local peoples. They ruthlessly crushed rebellion and revolt when necessary. Roman policy was to deal with such rebellion harshly - firstly, as a warning to others what the consequences were, and secondly the slaughter, enslavement,and confiscation of property of rebels on a wide scale severely diminished the numbers and resources available for any potential future uprisings.
Life in Roman Britain
What was it like to be in the Roman army?
(Original source of video: youtube)
Only men could be in the Roman Army. Every Roman soldier was a Roman citizen. He had to be at least 20 years old. He was not supposed to get married while he was a soldier. Most soldiers in the Roman Empire came from countries outside Italy. Soldiers had to stay in the army for at least 25 years. Then they could retire, with a pension or a gift of land to farm. Roman soldiers needed to go through tough trainings. They kept fit by running, marching and practice-fighting. They could march 20 miles (30 km) a day wearing armour. They could swim or cross rivers in boats, build bridges, and smash their way into forts. Each man carried his weapons and shield, some food and camping equipment (such as spare clothes, cooking pot and an axe or spade).
What luxury items/interesting inventions did the Romans bring to Britain?
Some examples of things that Romans introduced to Britain that are still in use today:
| Architecture | Art | Literature | Language (Latin) |
| Sanitation (sewage) |
Aqueducts | Education | Irrigation ( water supply) |
| The calendar | Coins | Cement and bricks | Public heated baths |
| Turnips and carrots | Paved streets and pavements | Apples, pears and grapes | Benefits (free food) for poor citizens |
| Roads | Wine | Cats | Stinging nettles |
| Towns | Glass | Street Cleaners | Shops |
| Laws | Tenement Blocks | Public order | Firemen and Police |
| Parks | Cabbages & peas | Public libraries | Public notices and advertisements |
How did Roman roads change Britain?
It was important for the Roman army to be able to move soldiers and all their baggage around the country. They built roads as straight as possible, in order to travel as quickly as they could. The roads connected forts and important towns. The Romans used the network of roads and also waterways to transport goods and facilitate trade from one country to another. Many of the Britain's modern day roads are in the same place as Roman ones.
Walk through a Roman street
Drop all the people and objects which don't belong to Roman period into the Time Tunnel! Do you know which period they really belong to?